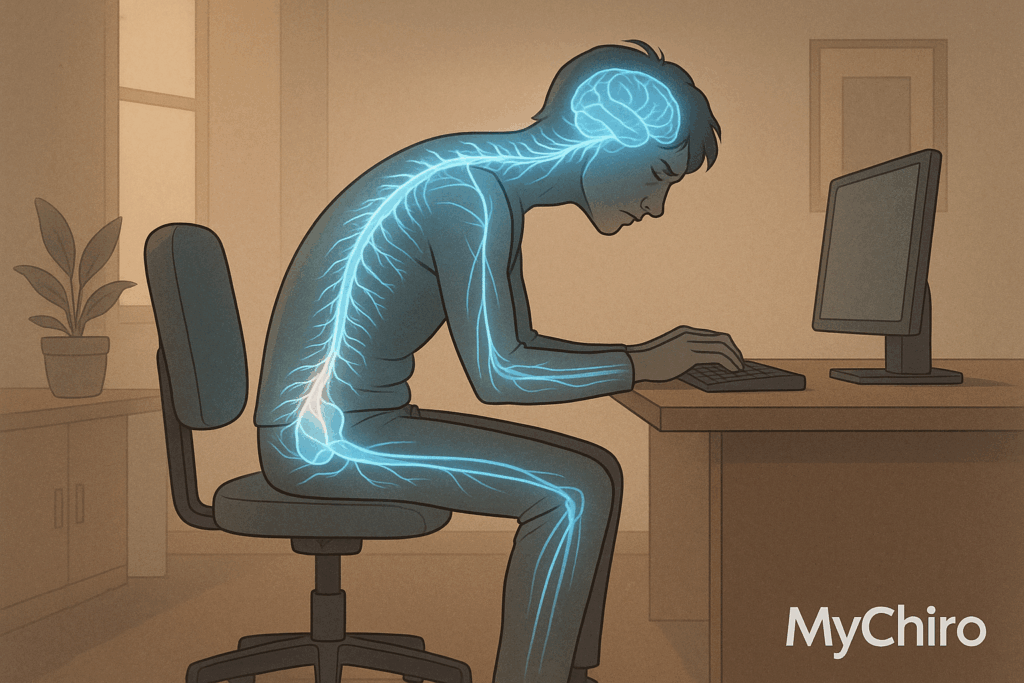
Posture refers to the way you hold your body. Good posture helps you align the head, shoulders, hips, and knees to reduce stress on bones and joints. Proper posture strengthens core muscles; it allows the body to move more efficiently while supporting stability. Because posture affects muscle engagement and joint stress, maintaining proper alignment can help reduce discomfort; it supports overall musculoskeletal health. Maintaining good posture may not prevent all spinal fractures, but it helps reduce stress on the vertebrae and surrounding muscles, and it can make recovery easier if a spine fracture occurs.
Understanding Posture
Good posture keeps everything in alignment while sitting, standing, and moving. Maintaining proper alignment reduces stress on bones and joints; it allows muscles to function efficiently during daily activity. Core muscles support spinal alignment, which improves stability; strengthening these muscles contributes to better balance and overall physical performance. Practicing proper posture helps maintain spinal health, and it can make everyday movements feel easier over time.
A spine fracture, particularly vertebral compression fractures, can occur when bones are weakened by conditions like osteoporosis, and they often happen during routine activities. These fractures may cause pain and limit mobility, but timely medical care can stabilize the spine and improve function. Because posture reduces unnecessary stress on the vertebrae, maintaining proper alignment supports overall spinal health, and it may make recovery easier if a fracture occurs.
Maintaining good posture also supports lung function and breathing efficiency. When the spine and shoulders are aligned properly, the chest can expand fully; breathing becomes easier during daily activities. Although this benefit may seem minor compared with structural support, proper posture contributes to overall wellness, and it can improve energy levels while reducing tension in the back and neck.
Understanding Spine Fracture
A vertebral compression fracture is a break in a vertebra, most often occurring in the thoracic or lumbar spine. These fractures may result from trauma or weakened bones due to osteoporosis; they can cause significant pain and limit mobility. Even normal daily activities can lead to fractures when bones are fragile; patients often experience decreased function until the fracture is treated. Because vertebral compression fractures affect stability and comfort, timely medical evaluation is important; treatment can help restore function.
Understanding Treatment Options
Treatment for vertebral compression fractures can include physical therapy, bracing, or vertebral augmentation. Bracing helps stabilize the spine and reduce movement that may worsen the fracture, and physical therapy strengthens supporting muscles to improve mobility. Vertebral augmentation involves injecting bone cement into the fractured vertebra, and it stabilizes the bone to relieve pain and restore function. Although each treatment targets different aspects of fracture management, combining approaches is often recommended for optimal recovery, and healthcare providers determine the best plan based on individual needs.
Talk to a Specialist
Maintaining good posture and understanding vertebral compression fractures are important components of musculoskeletal health. Good posture reduces stress on bones and joints, and it engages muscles that support stability. Vertebral compression fractures can result from trauma or osteoporosis, and timely treatment helps restore function and relieve pain. By practicing proper posture and seeking appropriate care for fractures, individuals can support spinal health and maintain mobility over time. Talk to a specialist to learn more.